Collaboration with MCAD systems
Xpedition Layout facilitates the communication of design data to mechanical CAD systems using a ProSTEP-approved IDX data exchange standard. With this ECAD/MCAD collaboration, designers can communicate between disciplines at any time or frequency, keeping participants in their respective system’s comfort zone. The integration between Xpedition and NX has been optimized to include 3D model sharing, design intent, additional copper data and improved rigid/flex support.
Collaborate from within your environment
ECAD and MCAD designers can collaborate from within their native environments, eliminating the need to learn new tools.
3D visualization
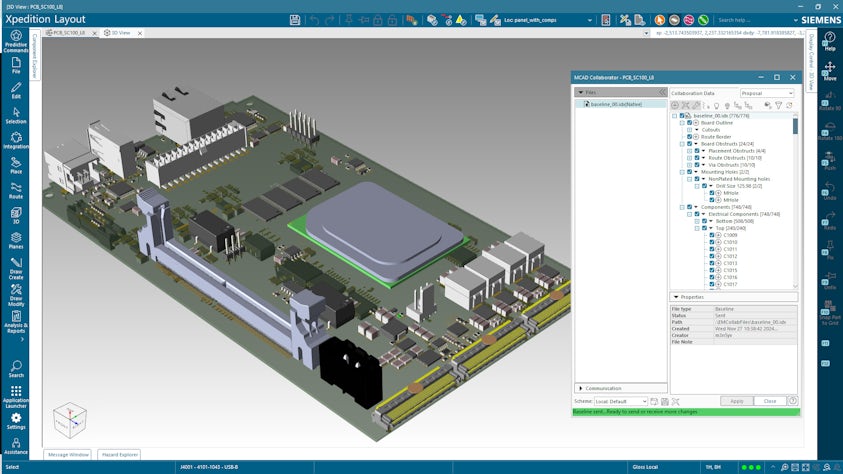
Visualization of the PCB and its enclosure within the layout environment allows designers to optimize the layout based on mechanical and manufacturability constraints.
Preview proposed changes
To clearly identify a proposed design change, designers highlight the proposed ECAD/MCAD collaboration object within the 3D viewer before applying the modification in their design. Consistent, iterative communication ensures team synchronization.
Dive deeper into this topic
Look for a methodology that enables context based, integral collaboration between the ECAD and MCAD domains. The value you’re going to get from that is that you have streamlined, integrated collaboration that minimizes the risk of errors during the data exchange. Read more in our ECAD/MCAD co-design blog or listen to our ECAD/MCAD co-design podcast.